李维达
L
 姓 名:李维达
姓 名:李维达
学 位:博士
导师情况:博士生导师
研究领域:干细胞与再生生物学;转分化;糖尿病药物开发
Email:liweida@tongji.edu.cn
通讯地址:上海市杨浦区四平路1239号,同济大学生命科学与技术学院522室,邮编200092
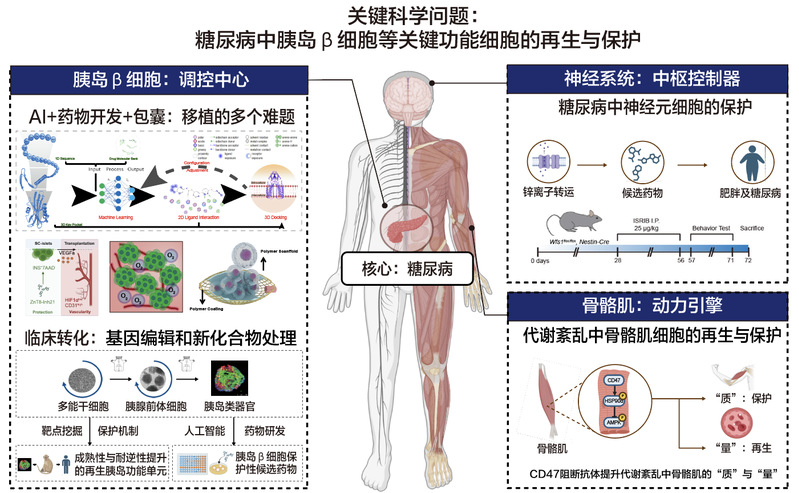
研究方向——糖尿病的再生医学与新药研发
1.诱导人多能干细胞为具有功能成熟性及长期稳定性的胰岛类器官,实现更先进的糖尿病干细胞疗法
2.重编程因子介导胰腺外分泌细胞向β细胞转化的体内机制研究
3.通过人类胰岛类器官和脑类器官进行糖尿病疾病及Wolfram综合征疾病模型的构建
4.以人类类器官为平台,进行糖尿病及神经退行性疾病的新型药物开发
5.代谢紊乱中骨骼肌细胞的再生与保护
个人简介:
李维达,长聘教授(青百A岗),博士生导师。本科毕业于南开大学,博士于北京大学及北京生命科学研究所联合培养,在哈佛干细胞研究所从事博士后研究期间获美国JDRF(青少年糖尿病基金)Fellowship Award(推荐人:Douglas Melton院士),2015年入选国家高层次青年人才计划,担任同济大学附属东方医院再生医学研究所及生命科学与技术学院教授,同时任教育部细胞干性与命运编辑前沿科学中心的PI。2016年作为首席科学家主持国家重点研发计划干细胞及转化专项青年项目“利用体内微环境实现糖尿病中胰岛细胞转分化再生的机制研究”,该项目立足于基础研究,着眼于转化医学。
研究方向围绕“糖尿病中β细胞再生”的重大科学问题进行深入研究:构建了高效胰腺转分化系统,提高了胰腺外分泌细胞转分化为胰岛β细胞的效率;通过基因编辑构建了具有抵抗糖尿病病理环境的功能化人类胰岛类器官,在糖尿病动物模型中实现了更高效、更稳定的治疗效果;解析了糖尿病中胰岛β细胞缺损的新机制。相关成果在 Nature Biotechnology、Nature Communications、Advanced Materials等知名学术期刊发表,并申请了多项发明专利。李维达教授与代谢专科、内分泌科等临床科室紧密合作,推动干细胞医学的临床转化。
课题组成员:
副教授2人,博士后3人,博士研究生11人,硕士研究生4人
主要科研项目:
1. 海外高层次引进人才计划,基于干细胞技术治疗糖尿病的细胞疗法,2016,主持
2. 国家重点研发计划干细胞及转化研究专项,利用体内微环境实现糖尿病中胰岛细胞转分化再生的机制研究,2016-2021,主持(首席科学家)
3. 国家自然科学基金面上项目,基于人胚胎干细胞诱导分化技术研究SLC30A8对人类胰岛β细胞功能成熟过程的调控机制,2019-2023,主持
4. 国家重点研发计划干细胞及转化研究专项,利用干细胞构建模拟早期胚胎发育和特定器官形成的系统,2020-2024,骨干
5. 国家自然科学基金面上项目,利用重编程因子实现体内胰腺外分泌细胞向β细胞转分化的机制研究,2022-2025,主持
6. 上海市2023年度“科技创新行动计划”细胞与基因治疗专项项目,基于人多能干细胞诱导的胰岛类器官研究人胰岛干细胞体外扩增技术,2023-2026,主持
7. 国家自然科学基金面上项目,基于人多能干细胞诱导分化技术研究WFS1通过调控锌离子转运实现对人胰岛β细胞的保护机制,2024-2027,主持
已获授权专利:
1.SLC30A8基因表达下调的抗糖尿病胰岛β细胞及其应用(ZL 2020 1 0157373.5)
2.一种改善Wolfram综合征中胰岛β细胞凋亡情况的药物(ZL 2021 1 0544764.7)
代表性论文:
Su Y*, Sun J*, Li X, Huang F, Kong Y, Chen Z, Zhang J, Qin D, Chen X, Wang Z, Pei Y, Gong M, Yang K, Xu M, Dong Y, He Q, Zhang ZN, Sheng Z, Deng Q, Wang H, Wang G, Hu P, Le R#, Gao S#, Li W#. CD47-blocking antibody confers metabolic benefits against obesity. Cell Rep Med. 2025 Apr 15:102089.
Hu R*, Ma Q*, Kong Y*, Wang Z, Xu M, Chen X, Su Y, Xiao T, He Q, Wang X, Xu W, Yang Y, Wang X, Li X, Liu Y, Chen S, Zhao R, Guo M#, Wang G#, Li W#. A Compound Screen Based on Isogenic hESC-Derived β Cell Reveals an Inhibitor Targeting ZnT8-Mediated Zinc Transportation to Protect Pancreatic β Cell from Stress-Induced Cell Death. Adv Sci. 2025 Apr 7:e2413161.
Gong M*, Fang Y*, Yang K, Yuan F, Hu R, Su Y, Yang Y, Xu W, Ma Q, Cha J, Zhang R, Zhang ZN#, Li W#. The WFS1-ZnT3-Zn2+ Axis Regulates the Vicious Cycle of Obesity and Depression. Adv Sci . 2024 Sep 11:e2403405.
Hu R*, Chen X*, Su Q*, Wang Z, Wang X, Gong M, Xu M, Le R, Gao Y, Dai P, Zhang ZN#, Shao L#, Li W#. ISR inhibition reverses pancreatic β-cell failure in Wolfram syndrome models. Cell Death Differ. 2024 Mar;31(3):322-334
Liu G*, Li Y*, Li M, Li S, He Q, Liu S, Su Q, Chen X, Xu M, Zhang ZN#, Shao Z#, Li W#. Charting a high-resolution roadmap for regeneration of pancreatic β cells by in vivo transdifferentiation from adult acinar cells. Sci Adv.1.2023 May 24;9(21):eadg2183.
Yuan F*, Li Y*, Hu R*, Gong M, Chai M, Ma X, Cha J, Guo P, Yang K, Li M, Xu M, Ma Q, Su Q, Zhang C, Sheng Z, Wu H, Wang Y, Yuan W, Bian S, Shao L, Zhang R, Li K, Shao Z#, Zhang ZN#, Li W#. Modeling disrupted synapse formation in wolfram syndrome using hESCs-derived neural cells and cerebral organoids identifies Riluzole as a therapeutic molecule. Mol Psychiatry.2023 Apr;28(4):1557-1570.
Ma Q*, Xiao Y*, Xu W*, Wang M, Li S, Yang Z, Xu M, Zhang T, Zhang ZN, Hu R, Su Q, Yuan F, Xiao T, Wang X, He Q, Zhao J, Chen ZJ, Sheng Z, Chai M, Wang H, Shi W, Deng Q#, Cheng X#, Li W#. ZnT8 loss-of-function accelerates functional maturation of hESC-derived β cells and resists metabolic stress in diabetes. Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 16;13(1):4142.
本论文获得Nature Review Endocrinology及Science Signaling的亮点评述,Nature Reviews Endocrinology杂志指出“这一工作证明了一种再生胰岛β细胞的新的途径,通过胰岛β细胞的再生来治疗糖尿病的前景已不再遥远”。同时Science signaling杂志也以此工作为亮点,指出该工作“促进了β细胞的成熟和功能,证明了再生的细胞可以长期稳定存在”。
相关亮点评述论文:
*Baek AE. Stemming metabolic stress. Sci Signal. 2022 Jul 26;15(744):eade0564.
*Starling S. Optimising stem cells for diabetes mellitus therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022 Oct;18(10):588.Sun J*, Su Y*, Xu Y, Qin D, He Q, Qiu H, Zhuo J, Li W#. CD36 deficiency inhibits proliferation by cell cycle control in skeletal muscle cells. Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 30;13:947325.
Liu G*, Li Y*, Zhang T*, Li M*, Li S, He Q, Liu S, Xu M, Xiao T, Shao Z#, Shi W#, Li W#. Single-cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Sexually Dimorphic Transcriptome and Type 2 Diabetes Genes in Mouse Islet β Cells. Genomics ProteomicsBioinformatics. 2021 Jun;19(3):408-422.
Wang X*, Zhou R*, Xiong Y, Zhou L, Yan X, Wang M, Li F, Xie C, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Ding C, Shi K, Li W, Liu Y, Cao Z, Zhang ZN, Zhou S, Chen C, Zhang Y#, Chen L#, Wang Y#. Sequential fate-switches in stem-like cells drive the tumorigenic trajectory from human neural stem cells to malignant glioma. Cell Res. 2021 Jun;31(6):684-702.
Gong L, Cao L, Shen Z, Shao L, Gao S, Zhang C#, Lu J#, Li W#. Materials for Neural Differentiation, Trans-Differentiation, and Modeling of Neurological Disease. Adv Mater. 2018 Apr;30(17):e1705684.
Cao L, Hu R, Xu T, Zhang ZN, Li W, Lu J. Characterization of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Human Serotonergic Neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 May 8;11:131.
Lv S, Li J, Qiu X, Li W, Zhang C, Zhang ZN#, Luan B#. A negative feedback loop of ICER and NF-κB regulates TLR signaling in innate immune responses. Cell Death Differ. 2017 Mar;24(3):492-499.
Lv S, Qiu X, Li J, Liang J, Li W, Zhang C, Zhang ZN, Luan B. Glucagon-induced extracellular cAMP regulates hepatic lipid metabolism. J Endocrinol. 2017 Aug;234(2):73-87.
Cavelti-Weder C*, Li W*, Zumsteg A, Stemann-Andersen M, Zhang Y, Yamada T, Wang M, Lu J, Jermendy A, Bee YM, Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC, Zhou Q. Hyperglycaemia attenuates in vivo reprogramming of pancreatic exocrine cells to beta cells in mice. Diabetologia. 2016 Mar;59(3):522-32.
Lv S, Qiu X, Li J, Li W, Zhang C, Zhang ZN, Luan B. Suppression of CRTC2-mediated hepatic gluconeogenesis by TRAF6 contributes to hypoglycemia in septic shock. Cell Discov. 2016 Dec 13;2:16046.
Cavelti-Weder C, Li W, Zumsteg A, Stemann M, Yamada T, Bonner-Weir S, Weir G, Zhou Q. Direct Reprogramming for Pancreatic Beta-Cells Using Key Developmental Genes. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2015 Mar 1;3(1):57-65.
Yamada T, Cavelti-Weder C, Caballero F, Lysy PA, Guo L, Sharma A, Li W, Zhou Q, Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC. Reprogramming Mouse Cells With a Pancreatic Duct Phenotype to Insulin-Producing β-Like Cells. Endocrinology. 2015 Jun;156(6):2029-38.
Li W*, Cavelti-Weder C*, Zhang Y*, Clement K, Donovan S, Gonzalez G, Zhu J, Stemann M, Xu K, Hashimoto T, Yamada T, Nakanishi M, Zhang Y, Zeng S, Gifford D, Meissner A, Weir G, Zhou Q. Long-term persistence and development of induced pancreatic beta cells generated by lineage conversion of acinar cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014 Dec;32(12):1223-30.
Li W*, Nakanishi M*, Zumsteg A, Shear M, Wright C, Melton DA, Zhou Q. In vivo reprogramming of pancreatic acinar cells to three islet endocrine subtypes. Elife. 2014 Jan 1;3:e01846.
Wang X, Li W, Zhao D, Liu B, Shi Y, Chen B, Yang H, Guo P, Geng X, Shang Z, Peden E, Kage-Nakadai E, Mitani S, Xue D. Caenorhabditis elegans transthyretin-like protein TTR-52 mediates recognition of apoptotic cells by the CED-1 phagocyte receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;12(7):655-64.
Li W, Zou W, Zhao D, Yan J, Zhu Z, Lu J, Wang X. C. elegans Rab GTPase activating protein TBC-2 promotes cell corpse degradation by regulating the small GTPase RAB-5. Development. 2009 Jul;136(14):2445-55.
Lu Q*, Zhang Y*, Hu T*, Guo P, Li W, Wang X. C. elegans Rab GTPase 2 is required for the degradation of apoptotic cells. Development. 2008 Mar;135(6):1069-80.
Cronican JJ, Beier KT, Davis TN, Tseng JC, Li W, Thompson DB, Shih AF, May EM, Cepko CL, Kung AL, Zhou Q, Liu DR. A class of human proteins that deliver functional proteins into mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. Chem Biol. 2011 Jul 29;18(7):833-8.
Zou W*, Lu Q*, Zhao D, Li W, Mapes J, Xie Y, Wang X. Caenorhabditis elegans myotubularin MTM-1 negatively regulates the engulfment of apoptotic cells. PLoS Genet.2009 Oct;5(10):e100067
Copyright© 2011-2015 生命科学与技术学院, All rights reserved
地址:上海市四平路1239号 电话:021-65981041 传真:65981041


