In recent years, single-cell multi-omics technologies have made groundbreaking progress, enabling scientists to perform multi-dimensional joint analyses of genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and spatial omics at single-cell resolution. These advances allow researchers to systematically construct comprehensive molecular maps of cells during processes such as development, differentiation, and disease progression. The availability of large-scale single-cell multi-modal datasets has made it possible to build predictive models of cell states based on multi-omics data, providing technical and data support for constructing virtual cells. However, the growing volume of multi-modal data has posed significant challenges, particularly in effectively integrating different molecular modalities and processing massive heterogeneous data to elucidate the complex regulatory mechanisms of cells. This has become a central challenge in the fields of single-cell multi-modal research and virtual cell construction.
Professor Qi Liu’s team from the Department of Bioinformatics, School of Life Sciences and Technology, Tongji University, has conducted systematic explorations in the development of AI algorithms for single-cell cross-modal integration. Previously, the team developed the scMVP algorithm, which integrates single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data using latent space joint embedding, as well as the UniTCR algorithm, which integrates T-cell transcriptome and TCR data for low-quality resources. Recently, Professor Qi Liu’s team published a paper titled “Benchmarking single-cell multi-modal data integrations” in Nature Methods. In this study, they introduced the Single Cell Multi-Modal Integration Benchmark (SCMMIB) platform, a comprehensive evaluation framework designed to provide a systematic, quantifiable, multi-scale, and multi-metric benchmarking platform for single-cell multi-modal integration algorithms. The platform evaluates 40 software solutions encompassing 65 integration algorithms, covering RNA, ATAC (DNA, high-dimensional), ADT (protein, low-dimensional), and spatial omics data. Based on the types of multi-modal data and dataset pairings, the platform designs six categories of evaluation tasks (Fig. 1).
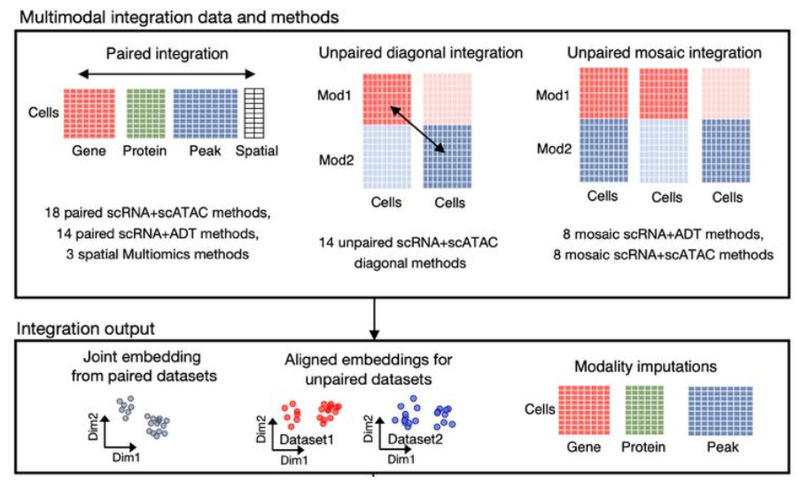
Fig. 1 Framework design of the SCMMIB platform
The platform establishes a three-dimensional evaluation framework and process for usability, accuracy, and stability tailored to different application scenarios of multi-modal integration (Fig. 2). The usability metrics assess whether algorithms can function properly across datasets of varying sizes (ranging from 500 to 500,000 cells) and on different hardware platforms (CPU/GPU acceleration). The accuracy metrics, which do not rely on gold-standard data for multi-modal integration, evaluate three hidden space metrics: biological structure preservation, batch effect removal, and cell alignment, as well as cross-modal generation accuracy. Stability metrics measure the consistency of algorithm performance and results across multiple runs and under varying data quality of different modalities.
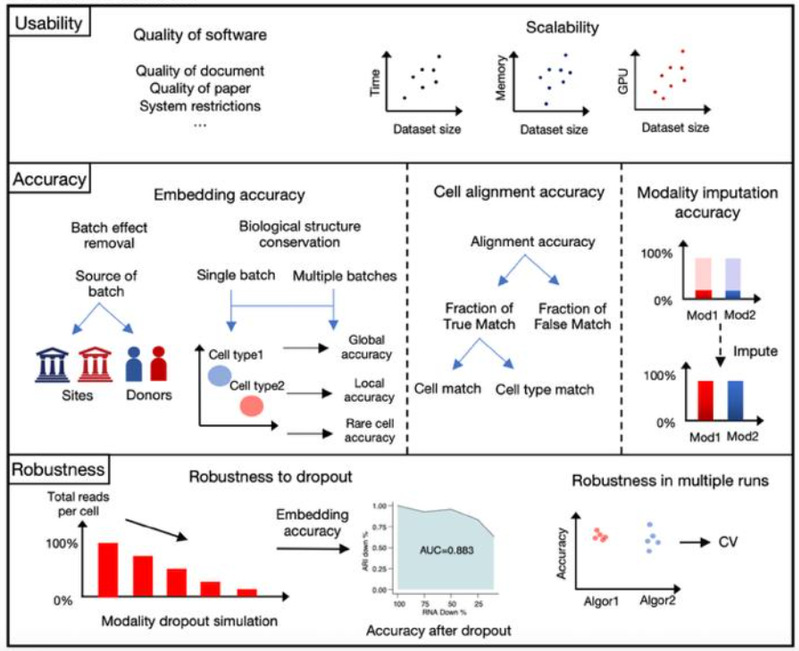
Fig. 2 SCMMIB platform evaluation process
For paired multi-modal integration tasks with fully matched modality information, the weighted nearest neighbor (WNN) algorithm from the popular Seurat toolkit exhibited the best overall performance in RNA + ATAC and RNA + ADT tasks, outperforming more complex deep learning models.
In tasks with partially or entirely unmatched modality information, several deep generative models showed remarkable performance. For partially matched mosaic integration tasks, the MIDAS algorithm demonstrated superior hidden space accuracy and stability. In cross-modal generation tasks, MIDAS significantly outperformed similar algorithms, achieving accuracy levels comparable to supervised multi-modal generation models (with 10% of the predictive modality as input). For completely unpaired diagonal integration tasks, the GLUE algorithm excelled in all modality alignment accuracy metrics, achieving alignment performance comparable to mosaic integration algorithms with partial pairing information. In spatial omics integration tasks, existing algorithms in the field did not exhibit significant advantages over classical analysis tools (e.g., Harmony, STAligner), highlighting the need for innovating spatial multi-omics integration methods.
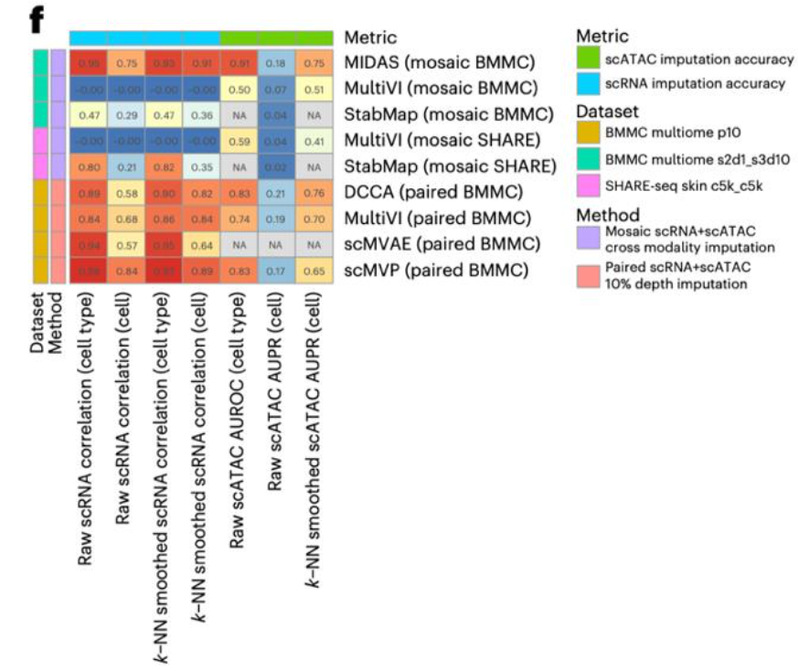
Fig. 3 Performance of mosaic integration and paired integration algorithms for cross-modal generation
In conclusion, the SCMMIB platform provides a systematic and comprehensive benchmarking framework for the field of single-cell multi-modal integration. Its evaluation results offer valuable reference points and guidelines for integrating single-cell DNA, RNA, protein, and spatial omics data, as well as for cross-modal biological knowledge discovery. This platform is expected to further promote in-depth research and applications in the field of single-cell cross-modal studies.
The first authors of the paper are Dr. Shaliu Fu and Ph.D. student Shuguang Wang, both from Professor Qi Liu’s research group at Tongji University’s School of Life Sciences and Technology. Professor Qi Liu is the corresponding author. The research received strong support from Professor Yawei Gao’s team at Tongji University’s School of Life Sciences and Technology. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Science Fund, Category A), the Shanghai Key Program for Computational Biology, and the Ministry of Education Frontier Science Center Program.
Paper Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02737-9